Pain and Disability from Hayward Whiplash Injury
Injuries after whiplash usually are not considered serious or threatening to an individual who was involved in a car accident. Drivers and passengers who complain of persistent pain symptoms from even a minor car accident would consider to have a “litigation neurosis” or L.T. Some studies have been done in order to prove if L.T. (conscious or unconscious exaggeration or fabrication of complaints) plays an important role in cervical spine acceleration/deceleration (CAD) cases. It has been proved that L.T. plays a significant role in the acceleration/deceleration traumas. As a matter of fact it has been proven that rear end collision has a much longer impact on the person’s life the previously thought.
The first and the most important factor that needs to be understood is the relationship of the amount of damage and injured driver or passenger. Often time a minor collision can cause a tremendous amount of soft tissue injuries to whoever was inside of the vehicle. For better understanding we must consider the deformation between elastic and plastic.
Instant deformation of the steel is considered to be elastic deformation and it is followed by a spring like reaction to the original shape. The transfer of energy is similar as cue ball in a billiard. The cue ball (in this case the vehicle which strikes the other) stops. The other ball (the vehicle which is rear-ended) is rapidly accelerated. The instant acceleration is the main cause of the injury.
When we look at plastic bumpers, the deformation there is most likely permanent. Steel absorbs the energy of the rear end collision. It collapses in on itself and stays there. For example, smashing two empty milk carton together. Plastic collision helps to minimize the injuries to occupants of the vehicle. This is what most of the drivers need when they get involved in a read end collision. When the force is not absorbed by a car it is absorbed by a driver and passenger.
Example: Forty five year old male who was at complete stop on a red light. Suddenly the other vehicle rear ended him at about eight miles per hour (this is a standard speed which is used to measure a “G-Force” of a rear-end collision. Often time the foot would be knocked off the brake and thus the vehicle would accelerate forward.
After the impact, his body is thrown backward. If headrest is present that would limit the hyperextension. However, many times the head-restrain is left in its lowest position. As a result, the formed fulcrum is going to cause even more injuries to a cervical spine.
Ramping is another phenomenon which must be taken into account. This is an upward motion toward the top of the seat which happens involuntarily upon impact. If the driver is tall, ramping may negate the effect of the headrest altogether, since his head will be thrown over the top of the seat.
When the driver of the vehicle is pushed back into his seat, his direction reverses. His chest and shoulders begin to move forward (note: his head is still pressed backwards.) At this point his head suddenly moves forward. In an eight miles per hours rear end collision the force equals to 5Gs. The shoulder harness, while saving him from serious head injuries, actually increases the likelihood of neck injuries by stopping the body – thereby increasing the relative speed of his head. (All of this takes place in approximately 3/10 of a second.
The force of impact goes beyond the tensile strength of the muscles and ligaments of the neck and back. These soft tissues are actually torn or medical term would be sprain and strain. Spinal nerves can also be injured or damaged. Traction injuries of the nerve roots are common (especially when the victims head was turned at the moment of impact). Compression of nerve roots often follows disc injury. (The swol1en disc traps the soft nerve between it and the bone.) An inflammatory process ensues in all of the soft tissues. If the force is great enough, compression fractures of the bones can occur.
Concussion (even without the head striking anything) is common. Damage to the temporomandibular joint is another injury common to these accidents.
15200 Hesperian Blvd., Ste. 104
San Leandro, CA, 94578
Call NOW for a FREE Consultation
(510) 481-2225

[…] Cars Prove to be the Least Effective in Preventing Whiplash Injuries. Numerous tests were done to measure the performance of the different car seats and head restraints […]
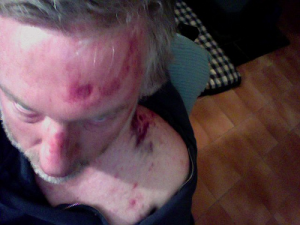
[…] whiplash can have devastating results in the future and lead to a long period of disability that lasts for […]
[…] Rear-end collisions are the major cause of whiplash injuries. It is because of the mechanics of the automobile crash. Rapid change of speed causes acceleration and deceleration of the cervical spine, thus forcefully moving head forward and backwards. Head restrain will help to reduce the effect of whiplash injury by ten percent. Even small fender bender will cause whiplash injuries and can create long lasting problems if not treated on time by your local chiropractic doctor. […]